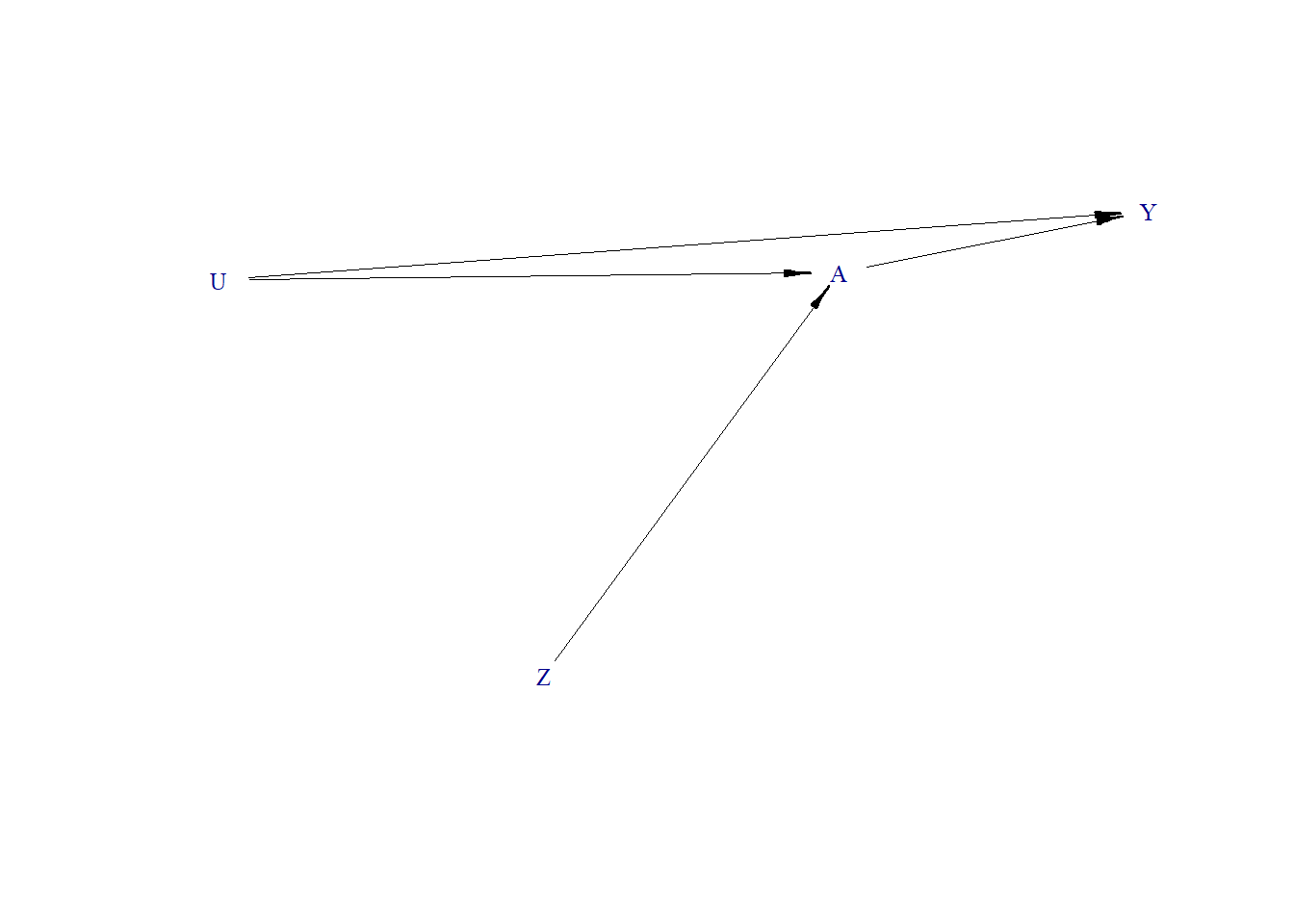
Z-bias
Z-bias occurs in the context of causal inference, specifically when using instrumental variables to estimate causal effects. Instrumental variables (IVs) are used to isolate the variation in the treatment variable that is unrelated to the confounding factors, thus providing a pathway to estimate causal effects.
Continuous Y
- U is unmeasured continuous variable
- Z is an instrumental variable
- A is binary treatment
- Y is continuous outcome
Non-null effect
- True treatment effect = 1.3
Data generating process
Generate DAG
Generate Data
Estimate effect
# True data generating mechanism (unattainable as U is unmeasured)
fit0 <- glm(Y ~ A + U, family="gaussian", data=Obs.Data)
round(coef(fit0),2)
#> (Intercept) A U
#> -1.0 1.3 3.0
# Unadjusted effect (Z not controlled)
fit1 <- glm(Y ~ A, family="gaussian", data=Obs.Data)
round(coef(fit1),2)
#> (Intercept) A
#> 0.79 5.59
# Bias fit 1
coef(fit1)["A"] - 1.3
#> A
#> 4.2935
# Adjusted effect (Z controlled)
fit2 <- glm(Y ~ A + Z, family="gaussian", data=Obs.Data)
round(coef(fit2),2)
#> (Intercept) A Z
#> 0.86 5.77 -0.12
# Bias from fit 2
coef(fit2)["A"] - 1.3
#> A
#> 4.465787Binary Y
- U is unmeasured continuous variable
- Z is an instrumental variable
- A is binary treatment
- Y is binary outcome
Non-null effect
- True treatment effect = 1.3
Data generating process
Generate DAG
Generate Data
Estimate effect
# True data generating mechanism (unattainable as U is unmeasured)
fit0 <- glm(Y ~ A + U, family="binomial", data=Obs.Data)
round(coef(fit0),2)
#> (Intercept) A U
#> -0.99 1.30 3.01
# Unadjusted effect (Z not controlled)
fit1 <- glm(Y ~ A, family="binomial", data=Obs.Data)
round(coef(fit1),2)
#> (Intercept) A
#> 0.40 3.02
# Bias fit 1
coef(fit1)["A"] - 1.3
#> A
#> 1.716482
# Adjusted effect (Z controlled)
fit2 <- glm(Y ~ A + Z, family="binomial", data=Obs.Data)
round(coef(fit2),2)
#> (Intercept) A Z
#> 0.51 3.29 -0.18
# Bias from fit 2
coef(fit2)["A"] - 1.3
#> A
#> 1.991396