
24 Application in MS
A recent article summarizes the estimated hazard ratios (HRs) for the association between exposure to any disease-modifying drug (DMD) and time from cohort entry (index date) to all-cause mortality among individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS) in British Columbia, Canada (1996–2017), using different methods of confounding adjustment (Karim et al. 2025).
- Unadjusted analysis suggested a strong protective effect (HR 0.31, 95% CI: 0.27–0.36).
- Investigator-specified covariate adjustment attenuated this effect (aHR 0.76, 95% CI: 0.65–0.89).
- High-dimensional propensity score (hdPS) methods further adjusted using empirically selected covariates:
- hdPS-1 to hdPS-3 yielded aHRs ranging from 0.77 to 0.80.
- High-dimensional disease risk score (hdDRS) methods produced similar estimates:
- hdDRS-1 to hdDRS-3 resulted in aHRs between 0.79 and 0.81.
Tip
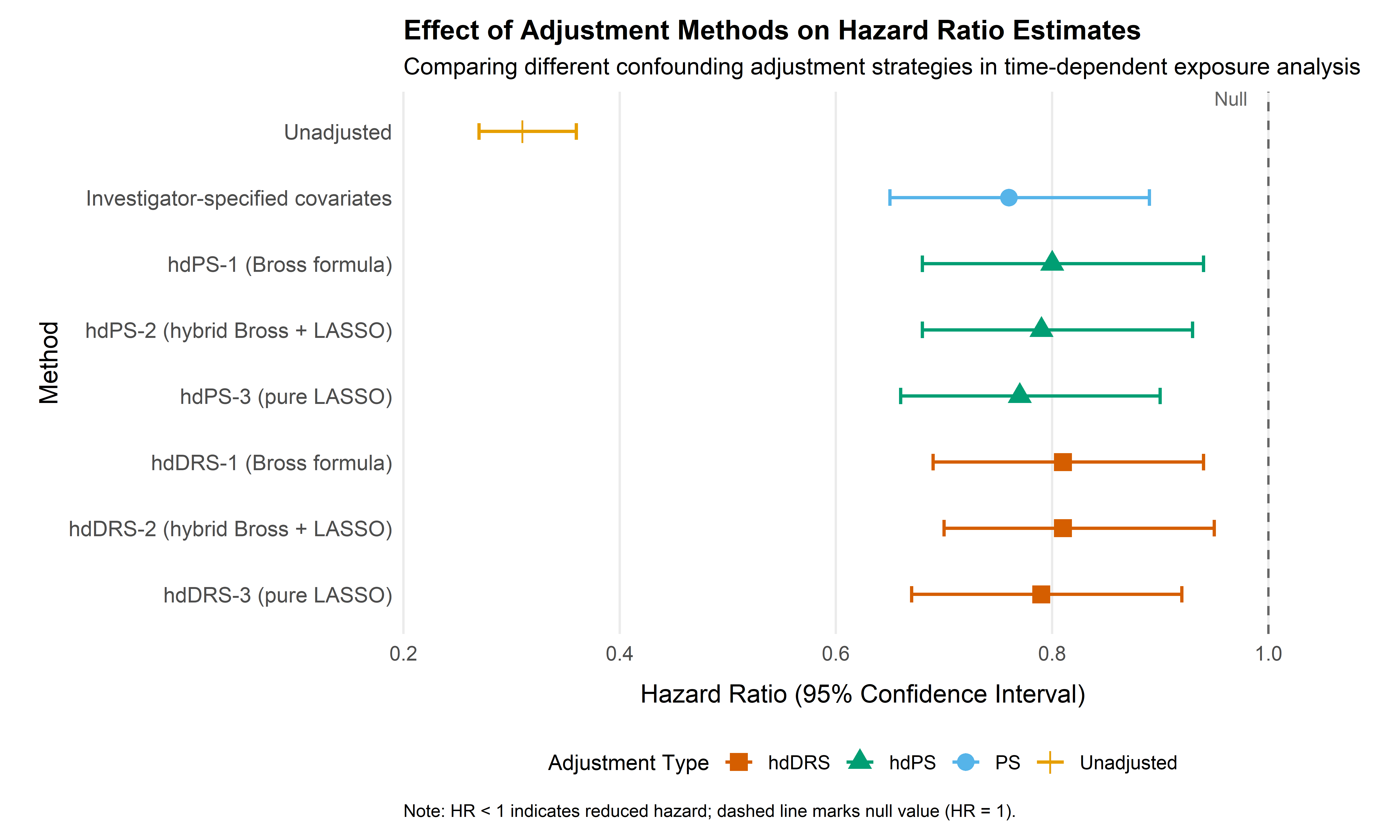
Despite adding high-dimensional proxy data, effect estimates changed only slightly from those using conventional covariate adjustment. These results suggest that residual confounding may be modest or that available proxies are insufficient to capture unmeasured confounders fully.