
13 Pure ML
Tip
We show an example using LASSO aproach
14 Pure ML approach (LASSO)
Start with all recurrence variables (EC in the following equation)
Say, 100 proxies (associated with outcome) were selected by LASSO approach (ML-hdPS)
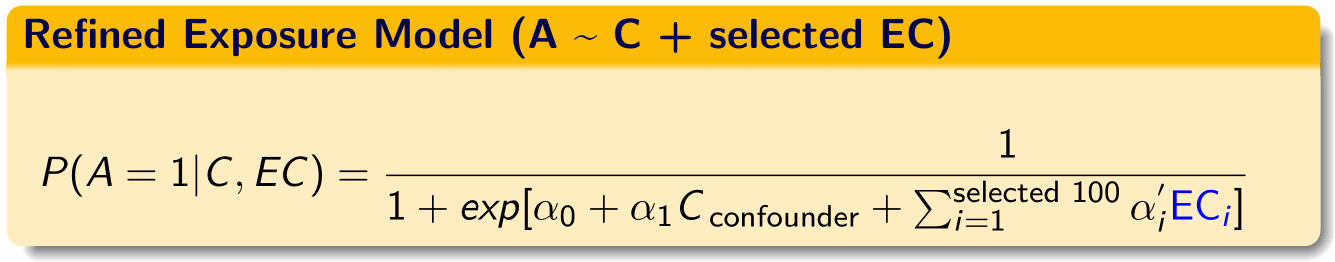
14.1 Choose variables associated with outcome
proxy.dim <- out2 # from step 3
dim(proxy.dim)
#> [1] 7585 143
proxy.dim$id <- proxy.dim$idx
proxy.dim$idx <- NULL
fullcovproxy.data <- merge(data.complete[,c("id",
outcome,
exposure,
investigator.specified.covariates)],
proxy.dim, by = "id")
dim(fullcovproxy.data)
#> [1] 3839 170
fullcovproxy.data$outcome <- as.numeric(I(fullcovproxy.data$diabetes=='Yes'))
fullcovproxy.data$exposure <- as.numeric(I(fullcovproxy.data$obese=='Yes'))proxy.list <- names(out2[-1])
# out3$autoselected_covariate_df[,-1] for hybrid
# out2 is from step2$recurrence_data
covarsTfull <- c(investigator.specified.covariates, proxy.list)
Y.form <- as.formula(paste0(c("outcome~ exposure",
covarsTfull), collapse = "+") )
covar.mat <- model.matrix(Y.form, data = fullcovproxy.data)[,-1]
lasso.fit<-glmnet::cv.glmnet(y = fullcovproxy.data$outcome,
x = covar.mat,
type.measure='mse',
family="binomial",
alpha = 1,
nfolds = 5)
coef.fit<-coef(lasso.fit,s='lambda.min',exact=TRUE)
sel.variables<-row.names(coef.fit)[which(as.numeric(coef.fit)!=0)]
proxy.list.sel.ml <- proxy.list[proxy.list %in% sel.variables]
length(proxy.list.sel.ml)
#> [1] 54- From all proxies, we try to identify proxies that are empirically associated with the outcome based on a multivariate LASSO (outcome with all proxies in one model).
- Note that LASSO model is choosing variables based on association with the
outcomeconditional on the ’exposure`. - Variable selection is only happening for proxy variables.
- Investigator specified variables are not being subject to variable selection.
14.2 Build model formula based on selected variables
covform <- paste0(investigator.specified.covariates, collapse = "+")
proxyform <- paste0(proxy.list.sel.ml, collapse = "+")
rhsformula <- paste0(c(covform, proxyform), collapse = "+")
ps.formula <- as.formula(paste0("exposure", "~", rhsformula))Build propensity score model based on selected variables based on LASSO.
14.3 Fit the PS model
hdps.data <- fullcovproxy.data
require(WeightIt)
W.out <- weightit(ps.formula,
data = hdps.data,
estimand = "ATE",
method = "ps")Propensity score model fit to be able to calculate the inverse probability weights.
14.4 Obtain log-OR from unadjusted outcome model
out.formula <- as.formula(paste0("outcome", "~", "exposure"))
fit <- glm(out.formula,
data = hdps.data,
weights = W.out$weights,
family= binomial(link = "logit"))
fit.summary <- summary(fit)$coef["exposure",
c("Estimate",
"Std. Error",
"Pr(>|z|)")]
fit.summary[2] <- sqrt(sandwich::sandwich(fit)[2,2])
require(lmtest)
conf.int <- confint(fit, "exposure", level = 0.95, method = "hc1")
fit.summary_with_ci <- c(fit.summary, conf.int)
knitr::kable(t(round(fit.summary_with_ci,2))) | Estimate | Std. Error | Pr(>|z|) | 2.5 % | 97.5 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.29 | 0.13 | 0 | 0.19 | 0.39 |
Summary of results (log-OR).